Governments and various institutions frequently operate systems without internet access. However, the RAMBO method allows for the transmission of data from the memory of isolated computers to the outside world.
According to a report by Dr. Mordechai Guri, a researcher at Ben-Gurion University in the Negev, Israel, isolated systems are not impervious to external threats. The researcher utilized the volatile memory of a computer to generate radio signals for data transmission. He termed this attack RAMBO (Radiation of Air-gapped Memory Bus for Offense).
“Malware on a compromised computer can create radio signals from the memory bus (RAM). By leveraging these signals, the malware can encode sensitive information, such as files, images, keystroke logs, biometric data, and encryption keys. With software-defined radio (SDR) hardware and a simple off-the-shelf antenna, an attacker can intercept the transmitted raw radio signals from a distance,” writes Mordechai Guri.
Theoretically, this technique could be exploited by attackers from the outside to intercept and steal confidential data without needing an internet connection or physical access to the system. In experiments, a transmission rate of 1000 bits per second was achieved, meaning it would take nearly 100 days to exfiltrate 1 GB of data. However, an attacker would still need to infect the target computer with malware to create such a radio transmitter.
“When data is transmitted over the RAM bus, it involves rapid changes in voltage and current, primarily on the data bus. These voltage fluctuations generate electromagnetic fields, which can emit electromagnetic energy through electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI),” the article states.
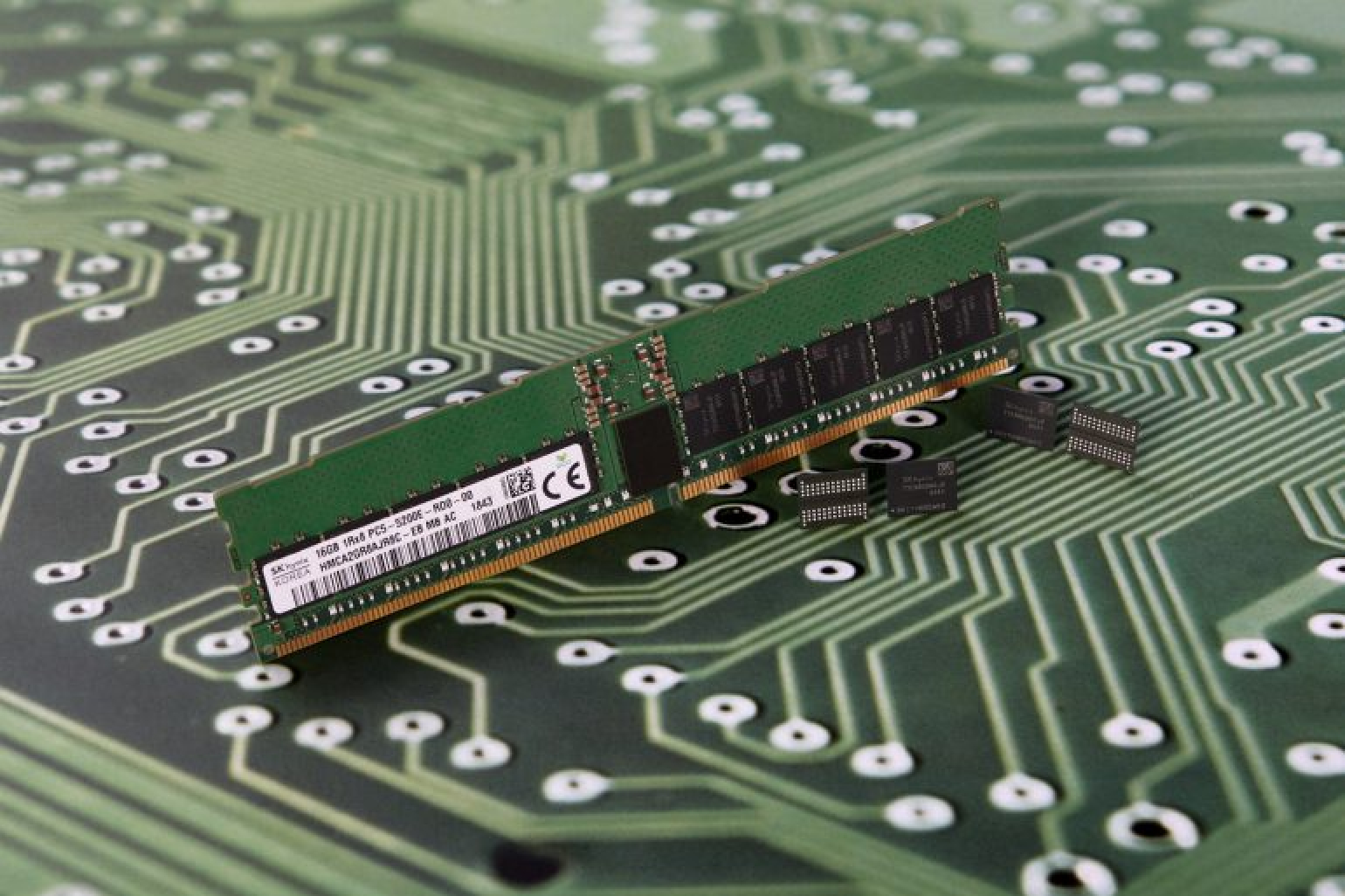
Using a computer equipped with an Intel Core i7 3.6 GHz processor and 16 GB of RAM operating within the frequency range of 2.133-2.400 GHz, Guri demonstrated that small files could be transmitted in approximately 400 seconds over a distance of 7 meters. The bandwidth is sufficient to run a keylogger in real time. Shorter distances would result in increased transmission speeds.
The publication suggests several countermeasures against such attacks: zone restrictions, host intrusion detection systems, external monitoring of the electromagnetic spectrum, memory activity blocking, radio emission suppression, and Faraday cages.
Source: Cybernews











Comments (0)
There are no comments for now