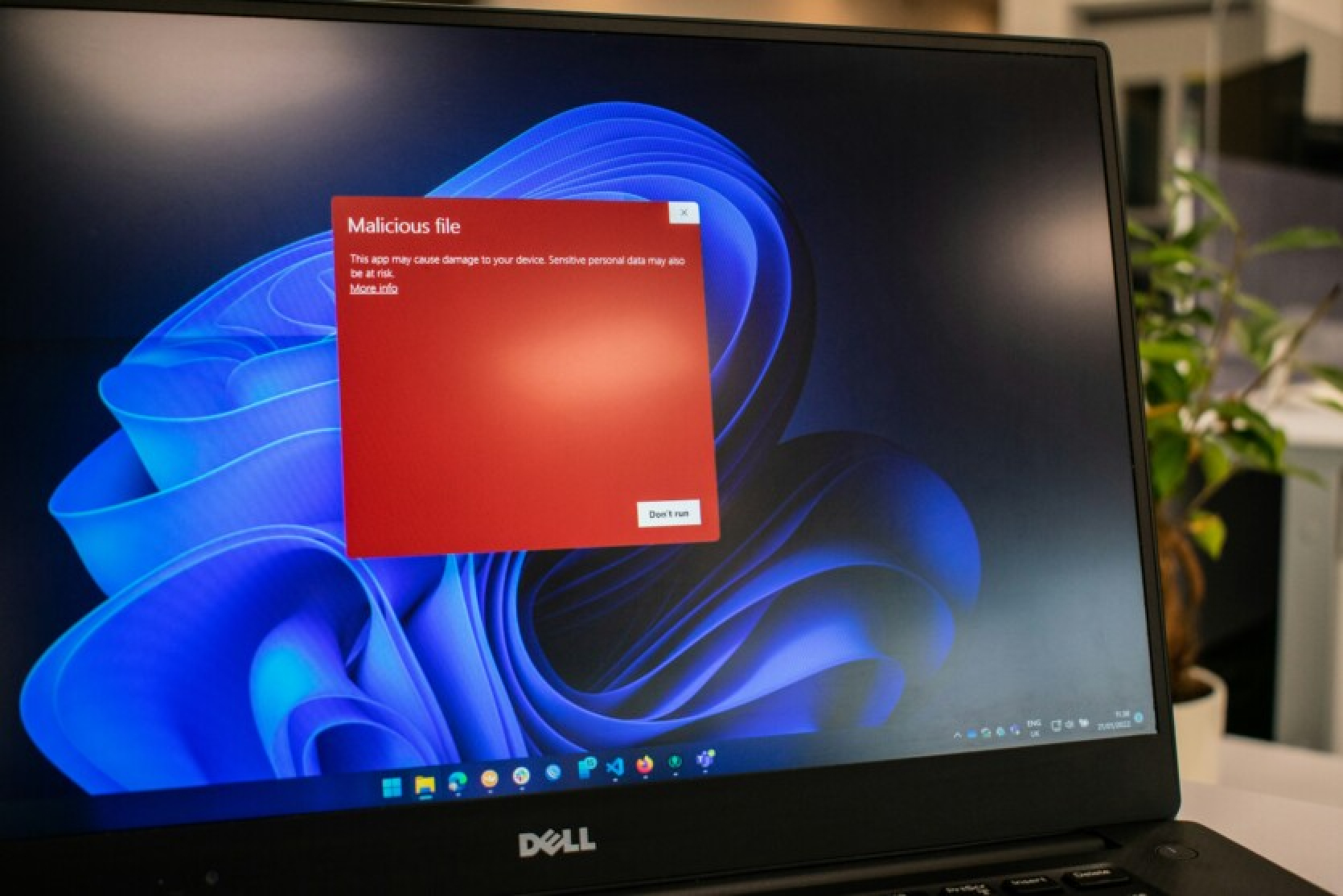
In August of this year, a significant number of cryptocurrency owners became targets of a new global cyberattack. The malicious software (malware) known as Clipper alters the address of the intended wallet during asset transfers to one controlled by hackers.
Malware Malware (short for malicious software) refers to software or code that damages devices, steals information, or provides unauthorized access. Clipper is not new. This malware was first detected in 2017 and can infect devices running Android and Windows. Clipper is capable of "reading" and then altering any text that the user has copied.
Malware (short for malicious software) refers to software or code that damages devices, steals information, or provides unauthorized access. Clipper is not new. This malware was first detected in 2017 and can infect devices running Android and Windows. Clipper is capable of "reading" and then altering any text that the user has copied.
According to a report from Kaspersky, as of March 2024, over 15,000 users in 52 countries have been affected. Hackers have shown particular interest in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and Monero.
A new wave of attacks was recorded on August 27, 2024, as reported by Binance.
How Clipper Malware Works
- Initially, the malware infiltrates the device through infected files or software vulnerabilities.
- The program then monitors the data copied by the user, which goes into the clipboard.
- Once the user copies a cryptocurrency wallet address, the malware replaces it with the address of the hacker’s wallet.
- If the user does not notice the swap in time, the cryptocurrency ends up in the hands of the fraudsters.
How to Protect Yourself from Malicious Software
- Download applications only from official sources.
- Carefully verify the wallet address before confirming a transaction.
- Install and regularly update antivirus software.
Source: eInfochips, Inc., Kaspersky, Binance












Comments (0)
There are no comments for now