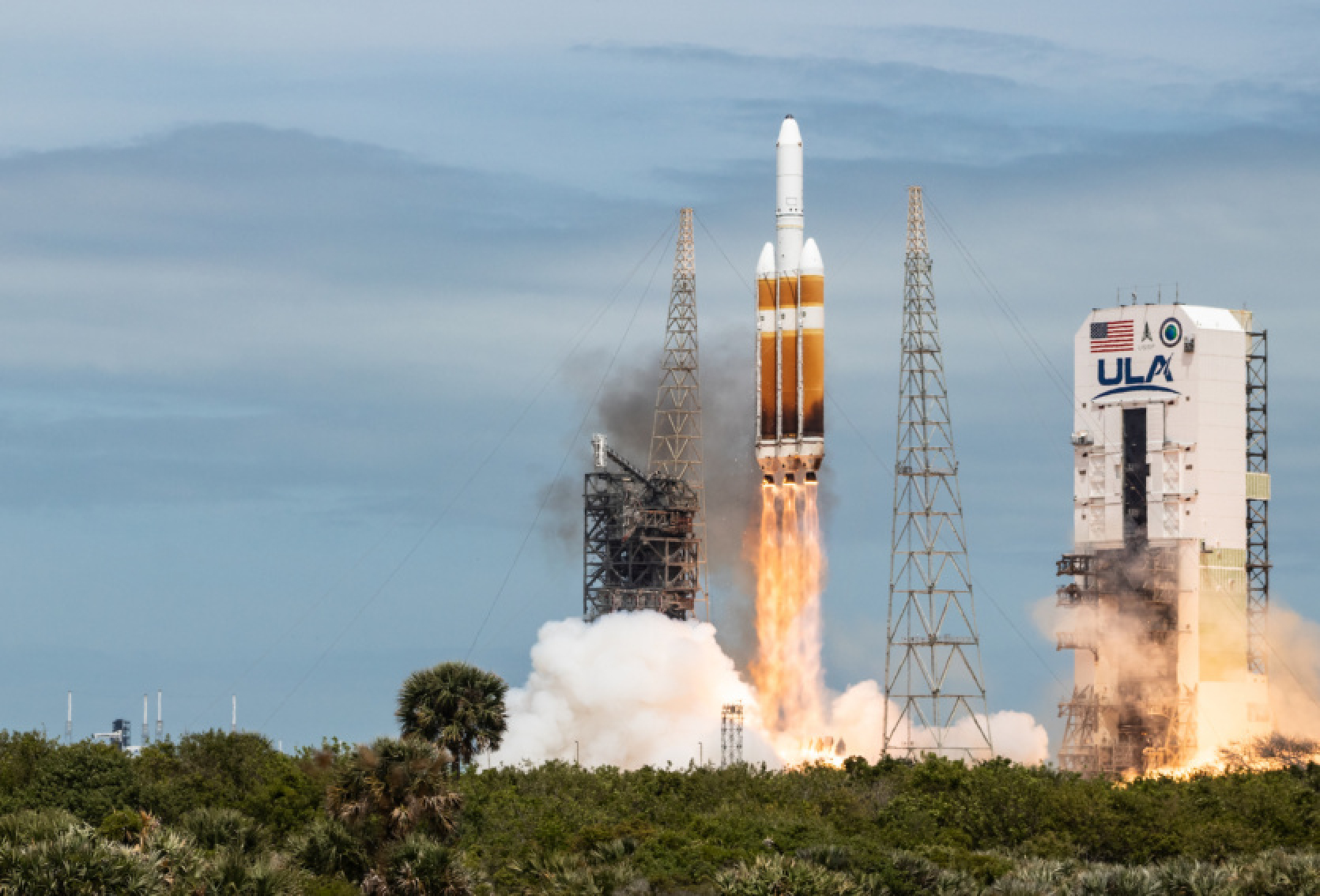
The evening of April 9, Delta IV Heavy completed its last mission and ended its 20-year flying career - the heavy carrier rocket ULA launched a classified military satellite into space for US reconnaissance (National Reconnaissance Office).
This launch marks the end of the Delta rocket series - in the future, their work will be taken over by Falcon and Vulcan rockets. In total, Delta IV family of rockets of five varieties flew into space 45 times over 22 years of operation.
As for Delta IV Heavy, which belongs to heavy-class rockets and was manufactured by American ULA, it is actually third in terms of maximum payload capacity among current launch vehicles. Like other Delta rockets, Delta IV Heavy is a product of United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture of Lockheed Martin and Boeing. The first launch of Delta IV Heavy took place in 2004 and was partially successful due to the satellites being placed in the wrong orbit.


Structurally, Delta IV Heavy rocket consists of two stages and two liquid boosters, as well as two payload fairing options. All engines operate on the fuel pair of "liquid oxygen - liquid hydrogen". The rocket is capable of delivering a payload of up to 13.8 tons to geostationary transfer orbit and up to 28.3 tons to low Earth orbit. Until April 9, the rocket had been launched 15 times - the main customers were the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and the US Space Force, but the flight list also includes several non-military missions, such as the first unmanned flight of the Orion spacecraft and the launch of the Parker Solar Probe into space.
Last Mission
Let's relive liftoff of the final #DeltaIVHeavy rocket carrying #NROL70 for the @NatReconOfc, closing Delta's six decade legacy of excellence in space! #TheDeltaFinalepic.twitter.com/wOuFFza2ac
— ULA (@ulalaunch) April 9, 2024
The launch was initially planned for March 28, but it was postponed twice, first due to weather conditions and then due to a malfunction of the pump on the nitrogen supply pipeline. The launch of Delta IV Heavy as part of the NROL-70 mission on April 9 was the sixteenth one - the rocket took off at 19:53 Kiev time from the SLC-37B launch pad at the US Space Force base at Cape Canaveral. All details of the NROL-70 mission are classified. Most likely, the payload is an electronic reconnaissance satellite that was sent into geostationary orbit.
It is worth remembering that a few months earlier, the European Ariane 5 rocket retired after flying for 27 years, and its replacement Ariane 6 is delayed due to a number of technological issues amid a general crisis in European rocket manufacturing.













Comments (0)
There are no comments for now